Thymus Gland Removal in Myasthenia Gravis: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the neuromuscular junction, leading to fluctuating muscle weakness and fatigue. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks acetylcholine receptors at the junction where nerve cells communicate with muscles. This condition can significantly impact a patient's quality of life, making daily activities challenging.
The Role of the Thymus Gland
The thymus gland is a small organ located behind the breastbone, playing a crucial role in the immune system. It is responsible for the development of T-cells, which are essential for the body's defense against pathogens. Interestingly, the thymus gland is often enlarged or abnormal in individuals with myasthenia gravis, suggesting its involvement in the disease's pathology.
Thymectomy: What is it?
Thymectomy refers to the surgical removal of the thymus gland. It has been shown to provide relief and improvement for many patients suffering from myasthenia gravis. The decision to perform a thymectomy usually depends on several factors, including the severity of the disease, age of the patient, and the presence of thymoma (a tumor of the thymus).
Benefits of Thymectomy in Myasthenia Gravis
- Reduction in Symptoms: Many patients experience a significant reduction in symptoms following thymectomy. This can lead to a substantial improvement in quality of life.
- Decreased Medication Dependence: After surgery, many patients are able to lower their dosages of immunosuppressive medications, or even discontinue them altogether.
- Improved Muscle Strength: Studies have shown that muscle strength often improves after the removal of the thymus gland, contributing to better physical function.
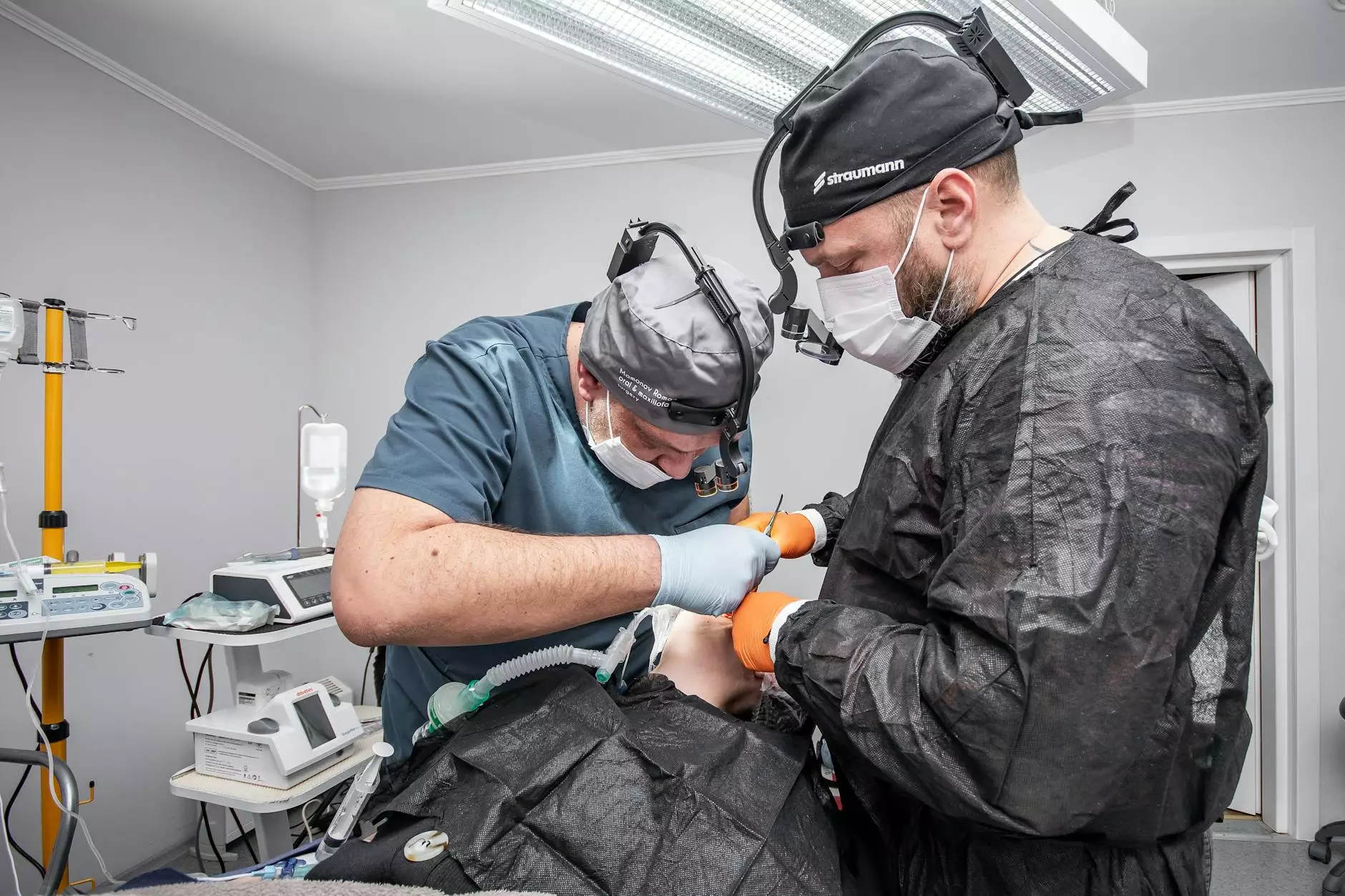
The Thymectomy Procedure
The surgical approach to thymus gland removal can vary depending on the patient's condition and the surgeon's preference. There are generally two methods: open thymectomy and minimally invasive thymectomy.
Open Thymectomy
During an open thymectomy, the surgeon makes a larger incision in the chest to gain access to the thymus gland. This technique allows for a thorough examination of the thymus and surrounding tissues but requires a longer recovery period due to the invasive nature of the procedure.
Minimally Invasive Thymectomy
Minimally invasive thymectomy can be performed using a video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) approach, which involves smaller incisions and the use of cameras and instruments to remove the thymus gland. This method typically results in less pain, a quicker recovery, and a shorter hospital stay.
Recovery After Thymectomy
The recovery process after thymus gland removal can vary based on the surgical technique used and the individual's overall health. Typical recovery includes:
- Hospital Stay: Patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days post-surgery for monitoring.
- Pain Management: Pain medications are prescribed to manage discomfort during recovery.
- Gradual Return to Activity: Patients are encouraged to gradually resume normal activities but should avoid strenuous exercise for several weeks.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up visits with the healthcare team are essential to monitor recovery and manage ongoing symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with thymectomy. These may include:
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the incision site or internally.
- Bleeding: Some patients may experience excessive bleeding during or after the surgery.
- Respiratory Issues: Patients with existing breathing difficulties may face challenges during recovery.
Long-Term Outcomes
Research has demonstrated that thymectomy can lead to long-term benefits for many patients with myasthenia gravis. Some studies indicate that surgical intervention can lead to a remission in symptoms or a long-lasting improvement in muscle strength. However, results can vary significantly among individuals.
Post-Thymectomy Management
After undergoing thymectomy, ongoing management of myasthenia gravis is crucial. Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as necessary and to monitor for any new symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thymus gland removal in myasthenia gravis patients represents a significant option for improving symptoms and enhancing quality of life. The procedure has gained recognition for its potential benefits and is often recommended for appropriate candidates. As with any medical intervention, it is essential for patients to discuss their options thoroughly with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of action tailored to their individual needs.
Learn More About Thymectomy at Neumark Surgery
If you or a loved one is suffering from myasthenia gravis and considering the options for treatment such as thymus gland removal, we encourage you to visit neumarksurgery.com for more information. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing comprehensive care and addressing your questions about the procedure and its implications for your health.
© 2023 Neumark Surgery. All rights reserved.
thymus gland removal myasthenia gravis








